Community Health Centers, most commonly known by their government acronym FQHC (Federally-Qualified Health Center), are one of the key pillars of America’s healthcare safety net. Often defined by serving at least 25% of uninsured patients as part of their patient mix, these organizations play a critical role in the communities they serve.
The first of these organizations were created almost 60 years ago and have historically provided very traditional primary and behavioral health care to a very underserved population. With dwindling government funding, an increase in competition, even in rural areas, many community health centers (CHCs) are rethinking their strategy that ensures not only their survival, but allows them to thrive in the communities they serve.
As CHC leaders strategizing how to best prepare their community health center for the future, they are pondering questions like the following:
- How can we improve patient outcomes through more effective patient care approaches?
- How can we bolster financial sustainability through novel business models and more diverse revenue sources?
- How can we strengthen our mission through new relationships within and outside our community?
- How can we succeed through the judicious and prudent use of innovative digital health technologies to succeed?
A Blueprint for the Future
In 2022, the Mid-Atlantic Telehealth Resource Center (MATRC) convened a group of health center leaders, representatives of healthcare government entities, national telehealth resource center leaders, and community health center experts to create a blueprint to offer Community Health Center leaders a valuable, pragmatic guide on how to prepare for and transform their organization into a “Health Center of the Future”.
Guided by the objective to create a “cohesive set of comprehensive insights and pragmatic recommendations across a wide spectrum of elements that describe the health center of the future coalescing the diverse expertise of a multidisciplinary team.”, the team set out over a number of months to tackle this ambitious goal.
Just like “all models are wrong, but some models are useful”, the same logic applies to a framework such as the one for the Health Center of the Future. In no way can a framework represent the complexities and intricacies of a Community Health Center.
But that also wasn’t the goal: Rather, the elegance of the model lies in simplifying the complexities of reality to make them easier to manage, easier to plan — and easier to act on.
The Framework’s Core
At the core of the framework are three key elements that define the fundamental but also the innovative aspects of what a Community Health Center of the Future is made of:





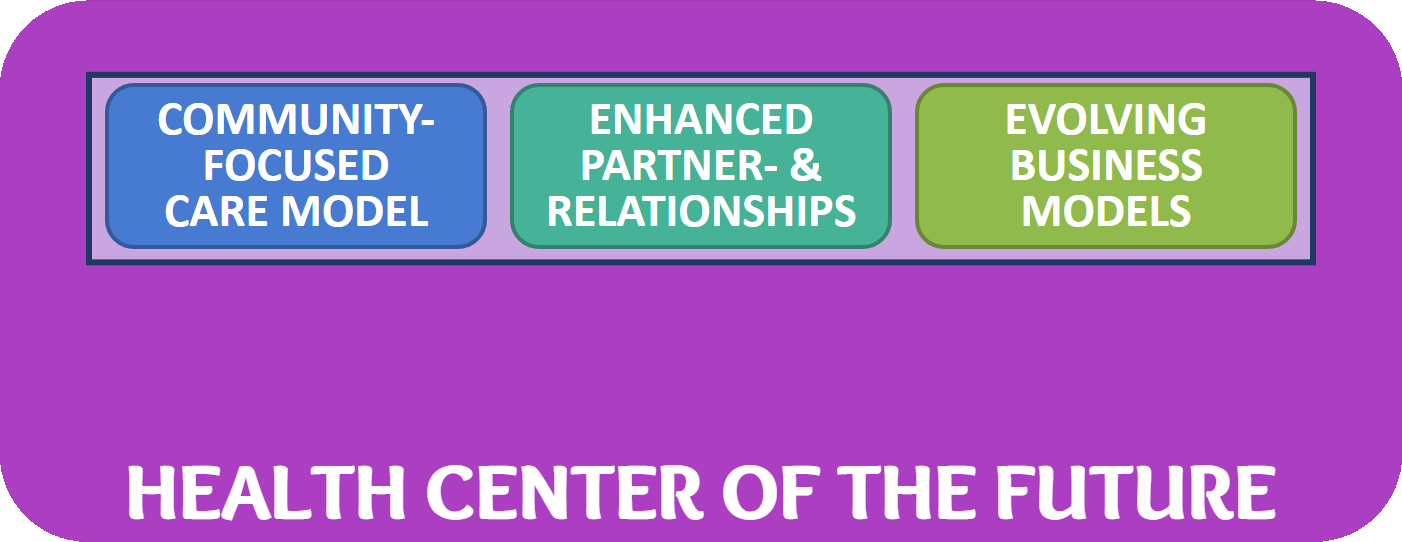


Community-Focused Care Model
This element of the framework recognizes that a care model must be built around the needs and the preferences of the community. A future-proof care model must address the population health needs of the community — informed and guided by actual data.
In addition, a modern care model recognizes the patients’ traditional preferences for trust and quality, but also the more recent desires of “the modern healthcare consumer” for value and convenience. Especially the convenience aspect must be reflected, e.g., through virtual and asynchronous care delivery modalities in a hybrid environment, a.k.a., telehealth for population health.
Enhanced Partnerships and Relationships
According to the second key element of the framework, at the heart of a sustainable Community Health Center of the Future lies a web of partnerships and relationships with partners within and beyond the community. With dwindling resources, partnerships and alliances create synergistic effects that amplify each partner’s unique abilities where 1 + 1 equals 3 or more.
As Einstein quipped: “The problems that exist in the world today cannot be solved by the same level of thinking that created them.” With our continuously improving understanding of the “Vital Conditions” that contribute to people’s health and well-being, it is clear that one organization cannot “go it alone”. The solution lies in strong relationships and partnerships with individuals and organizations. This includes, for example, a strong Health Center Board, partnerships with “social service” providers, and mutually beneficial sharing of expertise and insights with others that are serving the same population, etc.
Evolving Business Models
While Fee-for-Service reimbursement, through the prospective payment system (PPS) rate, is still the primary drive of revenue, many health centers have branched into other revenue streams, including pharmacy-based services (including 340B), value-based care arrangements, or grant funded opportunities.
To survive in the long run, without jeopardizing the mission of FQHCs to serve the uninsured and underinsured on a sliding scale, community health centers must develop sustainable alternative revenue streams, such as outcome based, capitated payment models for subpopulations, direct to consumer services, or arrangements with the private sector.
Expanding Beyond the Core
While the focus on these three core elements are pivotal to a successful Health Center of the Future, they are in themselves not sufficient. Rather, two fundamental elements that will enable the success of these three elements are missing to make the framework complete: Enabling and Supportive Technologies and High-Performance Capabilities.
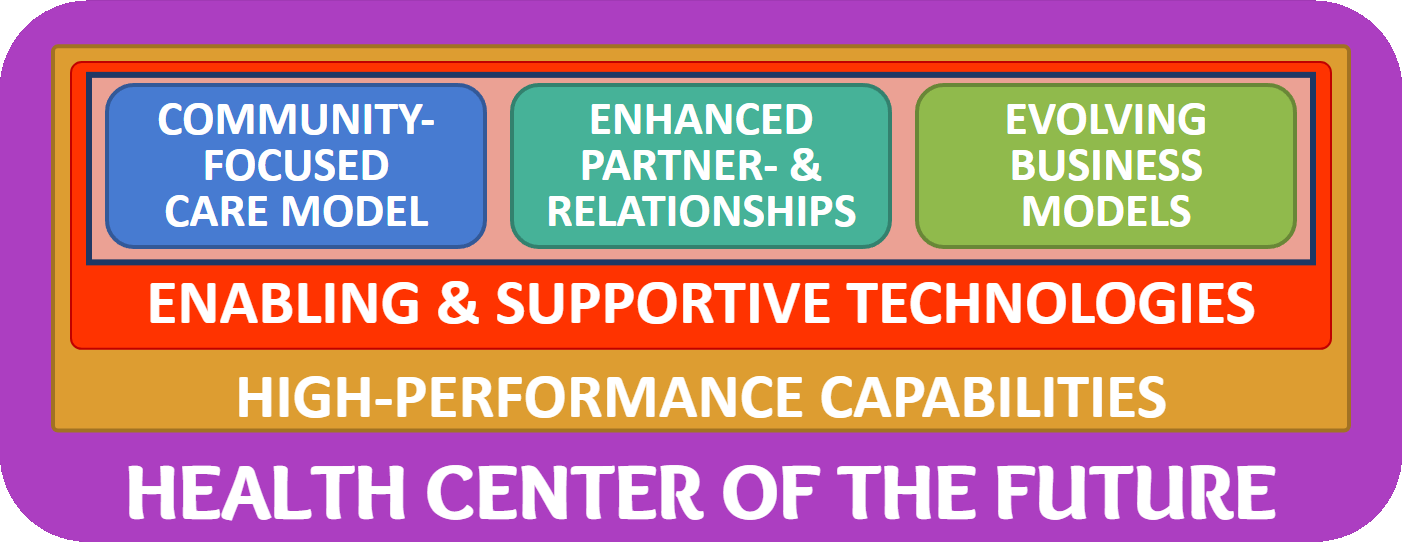


Enabling and Supportive Technologies


But it can be done and it has been done – as one amazing community-focused health center has demonstrated over and over again, year after year for multiple decades: The Southcentral Foundation in Alaska, a community-focused healthcare system serving the Alaskan Native and American Indian people.
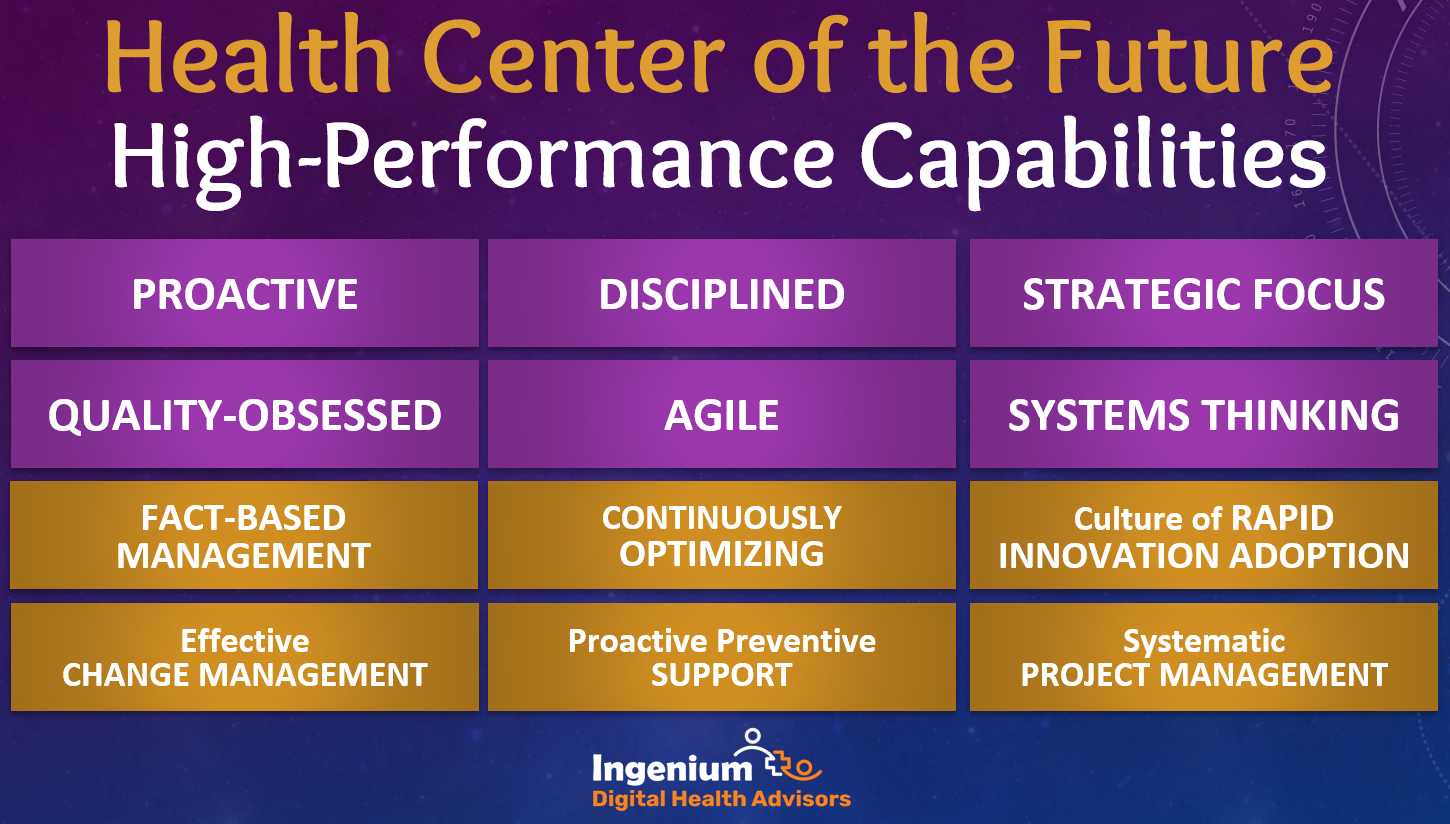
In a future article we will explore the whole set of high-performance capabilities which you can see in the graphic above.
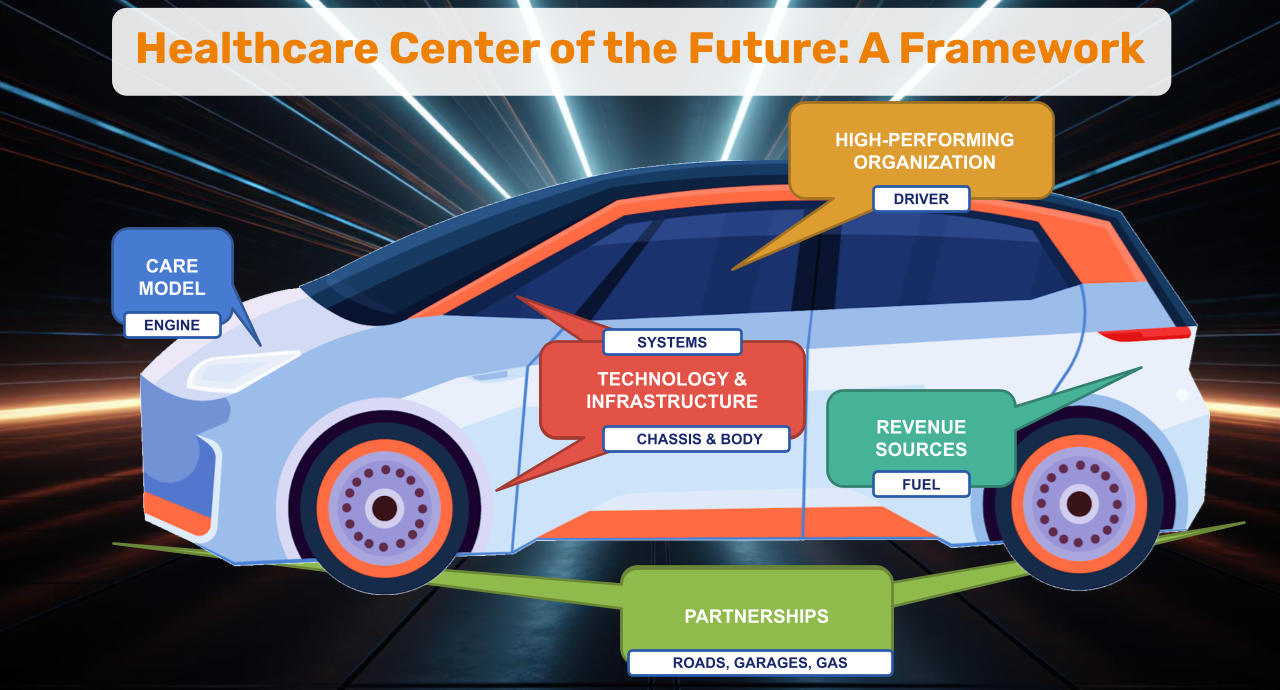
A Model for the HealthCARe Center of the Future
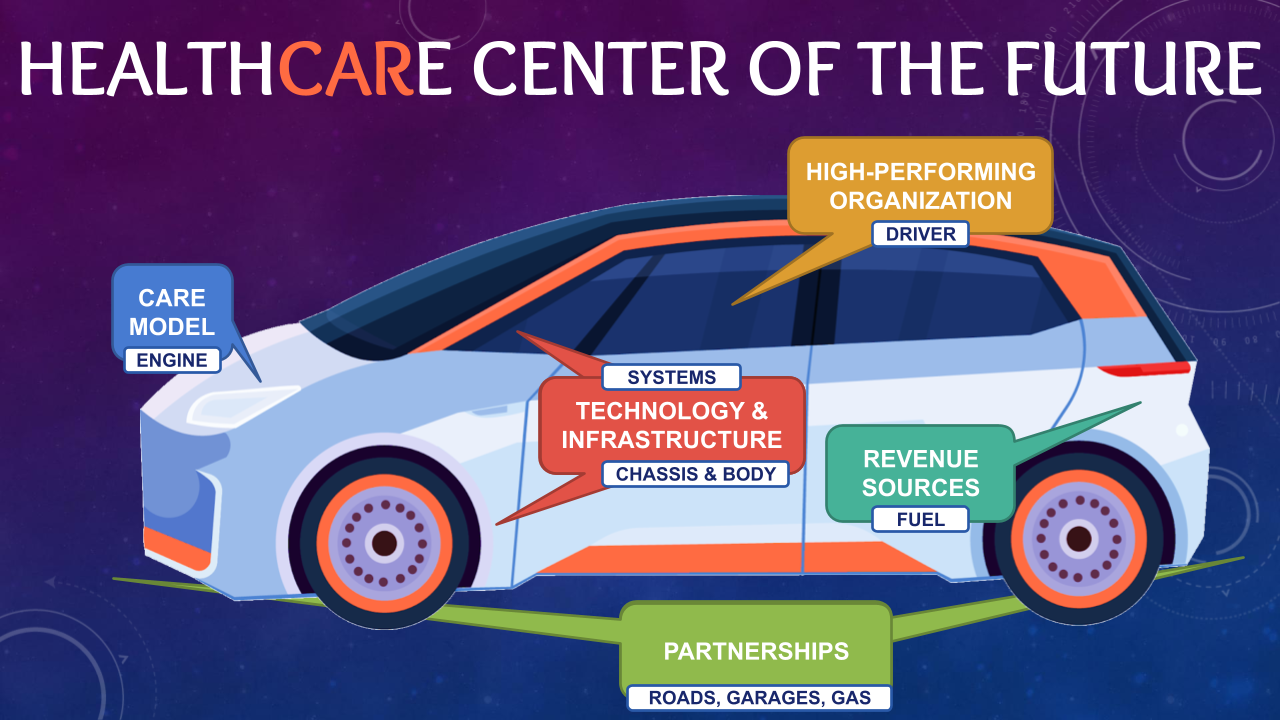


In our model, the Community-Focused Care Model is the Engine and the Evolving Business Models are the Fuel. The Enhanced Partnerships and Relationships are the environment in which the car operates, whereas the Enabling and Supportive Technology is represented by the systems and the chassis.
And at the steering wheel is the high-performing organization – because even the fastest and best equipped car will not go very far without a qualified driver.
Look for the future articles for more information on the technologies and high-performance capabilities. in the upcoming weeks.
Are you or is someone in your network working in a Community Health Center?
Then reach out to me for more information about the current “Health Center of the Future Training” initiative by the National Association of Community Health Centers (NACHC).










To receive articles like these in your Inbox every week, you can subscribe to Christian’s Telehealth Tuesday Newsletter.
Christian Milaster and his team optimize Telehealth Services for health systems and physician practices. Christian is the Founder and President of Ingenium Digital Health Advisors where he and his expert consortium partner with healthcare leaders to enable the delivery of extraordinary care.
Contact Christian by phone or text at 657-464-3648, via email, or video chat.